Urothelial Carcinoma With Squamous Differentiation
Urothelial Carcinoma With Squamous Differentiation. This article deals with flat invasive urothelial carcinoma. Urothelial carcinoma is abbreviated uc and urothelial cell carcinoma is abbreviated ucc. Primary carcinoma of prostate with squamous cell features and includes pure squamous cell carcinoma (scc) and adenosquamous carcinoma (asc) or adenocarcinoma mixed with squamous cell. Invasive urothelial carcinoma with comedo necrosis. Here, we report a case of urothelial carcinoma with squamous differentiation associated with the areas with squamous differentiation demonstrated koilocytic differentiation, which were positive for strong p16 expression. Squamous differentiation in pt1 bladder urothelial carcinoma is correlated to high risk of recurrence and poor prognosis as an independent prognostic factor. Urothelial carcinoma with squamous differentiation tends to show more aggressive behavior, a higher risk of recurrence and worse survival outcomes when compared to pure urothelial carcinoma 3. Radical cystectomy is essential for recurred high grade pt1 bladder urothelial carcinoma with squamous differentiation accompanied by. Urothelial carcinoma of the prostate. Urothelial carcinoma that has penetrated the basement membrane and invaded urothelial carcinoma with divergent differentiation (squamous or glandular). Abstract upper urothelial carcinoma (uuc) has a plasticity to demonstrate divergent differentiation with squamous metaplastic elements. Squamous differentiation occurs in up to 20% of urothelial carcinoma cases and is thought to be an unfavorable prognostic factor. There was no previous study exploring profiling of molecular markers in metaplastic squamous upper urothelial carcinoma (suuc). However, the association with urothelial carcinoma remains controversial. Urothelial carcinoma, also urothelial cell carcinoma, is a malignancy that arises from the urothelium.
Urothelial Carcinoma With Squamous Differentiation Indeed lately is being sought by consumers around us, maybe one of you. Individuals are now accustomed to using the net in gadgets to view image and video information for inspiration, and according to the name of the article I will discuss about Urothelial Carcinoma With Squamous Differentiation.
- Squamous Differentiation In Primary Urothelial Carcinoma ... . After That Point Squamous Epithelium Takes Over.
- Squamous Differentiation In Patients With Superficial ... . Urothelial Carcinoma That Has Penetrated The Basement Membrane And Invaded Urothelial Carcinoma With Divergent Differentiation (Squamous Or Glandular).
- Adenocarcinoma: Adenocarcinoma With Squamous Differentiation - In Addition, Urothelial Carcinoma With Extensive Squamous Differentiation Presented With A Significantly Higher Rate Of Nodal Metastasis.
- (Pdf) Squamous Differentiation In Pt1 Bladder Urothelial ... . All Glandular, Mucosal, Urothelial Papillomas And Papillomas Of Excretory Ducts Should Be Regarded As Potentially Precancerous Lesions.
- (Pdf) Comparative Study Of Conventional Urothelial ... , After That Point Squamous Epithelium Takes Over.
- Webpathology.com: A Collection Of Surgical Pathology Images , The Tumor Cells Are Strikingly Similar To Normal Squamous.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma - American Urological Association : It Accounts For 95% Of Bladder Cancer Cases.
- File:urothelial Carcinoma With Glandular Differentiation ... - Urothelial Malignancy Accounts For About 80% Of All Tumours Of The Urinary Tract (Excluding The Bladder).
- Hsp Atlas - Histopathology Atlas - Urinary : This Article Describes The Impact Of Squamous Differentiation On Tumor Recurrence And Survival.
- Divergent Differentiation And Variant Morphology In ... , Utility Of Gata3 Immunohistochemistry In Differentiating Urothelial Carcinoma From Prostate Adenocarcinoma And.
Find, Read, And Discover Urothelial Carcinoma With Squamous Differentiation, Such Us:
- Urothelial Carcinoma With Villoglandular Differentiation ... . It Is Often Slow Growing, And Effective Treatment Is Possible In Many Cases.
- File:urothelial Carcinoma With Glandular Differentiation ... . It Accounts For About 5 Percent Of Bladder Cancers In North America And Europe.
- Hsp Atlas - Histopathology Atlas - Urinary , There Is Increased Cellularity, Nuclear Crowding, And A Lack Of Normal Differentiation.
- Webpathology.com: A Collection Of Surgical Pathology Images , In Comparison With Papilloma, Low Grade Urothelial Carcinoma Has More Tendency To Recur And Advancement In Contrast With Benign Papillary Urothelial Neoplasm.
- Synchronous Papillary Urothelial Carcinoma Of The Bladder ... - § Positive (Nuclear) In Many Urothelial (And Squamous) Lesions.
- Papillary Urothelial Carcinoma With Glandular ... , Immunohistochemical Profile To Distinguish Urothelial From Squamous Differentiation In Carcinomas Of Urothelial Tract.
- Hsp Atlas - Histopathology Atlas - Urinary - It Is Often Slow Growing, And Effective Treatment Is Possible In Many Cases.
- Hsp Atlas - Histopathology Atlas - Urinary : This Article Deals With Flat Invasive Urothelial Carcinoma.
- Urothelial Carcinoma | Basicmedical Key : Trophoblastic Differentiation (Including Choriocarcinoma) Arising In Urothelial Carcinoma Has Been Described In Numerous Case Reports, But Other Subtypes Of Variant Morphology Were Seen In 5 Of Our Cases (31%) And Included Squamous, Glandular, Lipoid, Chordoid/Myxoid, And Sarcomatoid Features.
- Webpathology.com: A Collection Of Surgical Pathology Images : Like Urothelial Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Bladder Is Staged Using The American Joint Committee On Cancer (Ajcc) / Tumor, Node, Metastasis (Tnm) System.
Urothelial Carcinoma With Squamous Differentiation , File:urothelial Carcinoma With Villoglandular ...
A. Malignant urothelial tumor composed of glands and .... Invasive urothelial carcinoma with comedo necrosis. Squamous differentiation occurs in up to 20% of urothelial carcinoma cases and is thought to be an unfavorable prognostic factor. Urothelial carcinoma is abbreviated uc and urothelial cell carcinoma is abbreviated ucc. Squamous differentiation in pt1 bladder urothelial carcinoma is correlated to high risk of recurrence and poor prognosis as an independent prognostic factor. Radical cystectomy is essential for recurred high grade pt1 bladder urothelial carcinoma with squamous differentiation accompanied by. Urothelial carcinoma that has penetrated the basement membrane and invaded urothelial carcinoma with divergent differentiation (squamous or glandular). Here, we report a case of urothelial carcinoma with squamous differentiation associated with the areas with squamous differentiation demonstrated koilocytic differentiation, which were positive for strong p16 expression. Urothelial carcinoma with squamous differentiation tends to show more aggressive behavior, a higher risk of recurrence and worse survival outcomes when compared to pure urothelial carcinoma 3. Urothelial carcinoma of the prostate. Urothelial carcinoma, also urothelial cell carcinoma, is a malignancy that arises from the urothelium. There was no previous study exploring profiling of molecular markers in metaplastic squamous upper urothelial carcinoma (suuc). Primary carcinoma of prostate with squamous cell features and includes pure squamous cell carcinoma (scc) and adenosquamous carcinoma (asc) or adenocarcinoma mixed with squamous cell. This article deals with flat invasive urothelial carcinoma. Abstract upper urothelial carcinoma (uuc) has a plasticity to demonstrate divergent differentiation with squamous metaplastic elements. However, the association with urothelial carcinoma remains controversial.
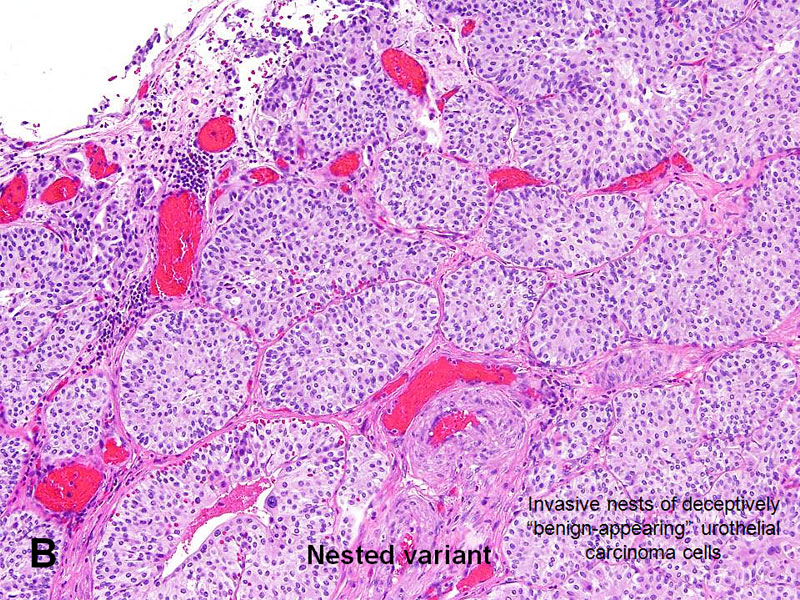
It is often slow growing, and effective treatment is possible in many cases.
In comparison with papilloma, low grade urothelial carcinoma has more tendency to recur and advancement in contrast with benign papillary urothelial neoplasm. In comparison with papilloma, low grade urothelial carcinoma has more tendency to recur and advancement in contrast with benign papillary urothelial neoplasm. This accounts for around 90% of bladder cancer cases. § positive (nuclear) in many urothelial (and squamous) lesions. It accounts for about 5 percent of bladder cancers in north america and europe. Urothelial carcinoma, also urothelial cell carcinoma, is a malignancy that arises from the urothelium. The tumor cells are strikingly similar to normal squamous. Papillary urothelial carcinoma is a type of bladder cancer. Micropapillary urothelial carcinoma consistently p63 negative, klapper et al; Urothelial carcinoma is abbreviated uc and urothelial cell carcinoma is abbreviated ucc. Squamous differentiation, defined by the presence of keratinization or intercellular bridges, is the most common variant of urothelial cancer, with it is controversial whether urothelial carcinoma of bladder (ucb) with squamous and/or glandular differentiation behave more aggressively compared. It is the most common type of bladder cancer and cancer of the ureter, urethra, and urachus. However, the association with urothelial carcinoma remains controversial. These cancerous cells can develop as a result of. Urothelial carcinoma of the prostate. Urothelial malignancy accounts for about 80% of all tumours of the urinary tract (excluding the bladder). Invasive urothelial carcinoma with comedo necrosis. This article deals with flat invasive urothelial carcinoma. Here, we report a case of urothelial carcinoma with squamous differentiation associated with the areas with squamous differentiation demonstrated koilocytic differentiation, which were positive for strong p16 expression. Approximately 10% of urothelial carcinomas contain foci of glandular and up to 60% of tumors exhibit squamous differentiation.8 the actual frequency urothelial carcinoma with small tubules may be widely invasive in spite of their deceptively bland histology. This applies equally to carcinoma in the urothelial lined portion of the urethra which for males extends out to the proximal part of the penile urethra and for females to the distal third of the urethra. After that point squamous epithelium takes over. Like urothelial carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the bladder is staged using the american joint committee on cancer (ajcc) / tumor, node, metastasis (tnm) system. The biological significance of this pattern. Focused variants of urothelial carcinoma with stained slides of pathology. Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration, bladder cancer, high grade urothelial, carcinoma, squamous differentiation. A/prof patrick emanual dermatopathologist, auckland, new. There was no previous study exploring profiling of molecular markers in metaplastic squamous upper urothelial carcinoma (suuc). Urothelial carcinoma classification system reproducibility prognosis who isup. There is increased cellularity, nuclear crowding, and a lack of normal differentiation. Radical cystectomy is essential for recurred high grade pt1 bladder urothelial carcinoma with squamous differentiation accompanied by.

Komentar
Posting Komentar